Battery Circuit Protection: How It Saves Your Phone & Gadgets
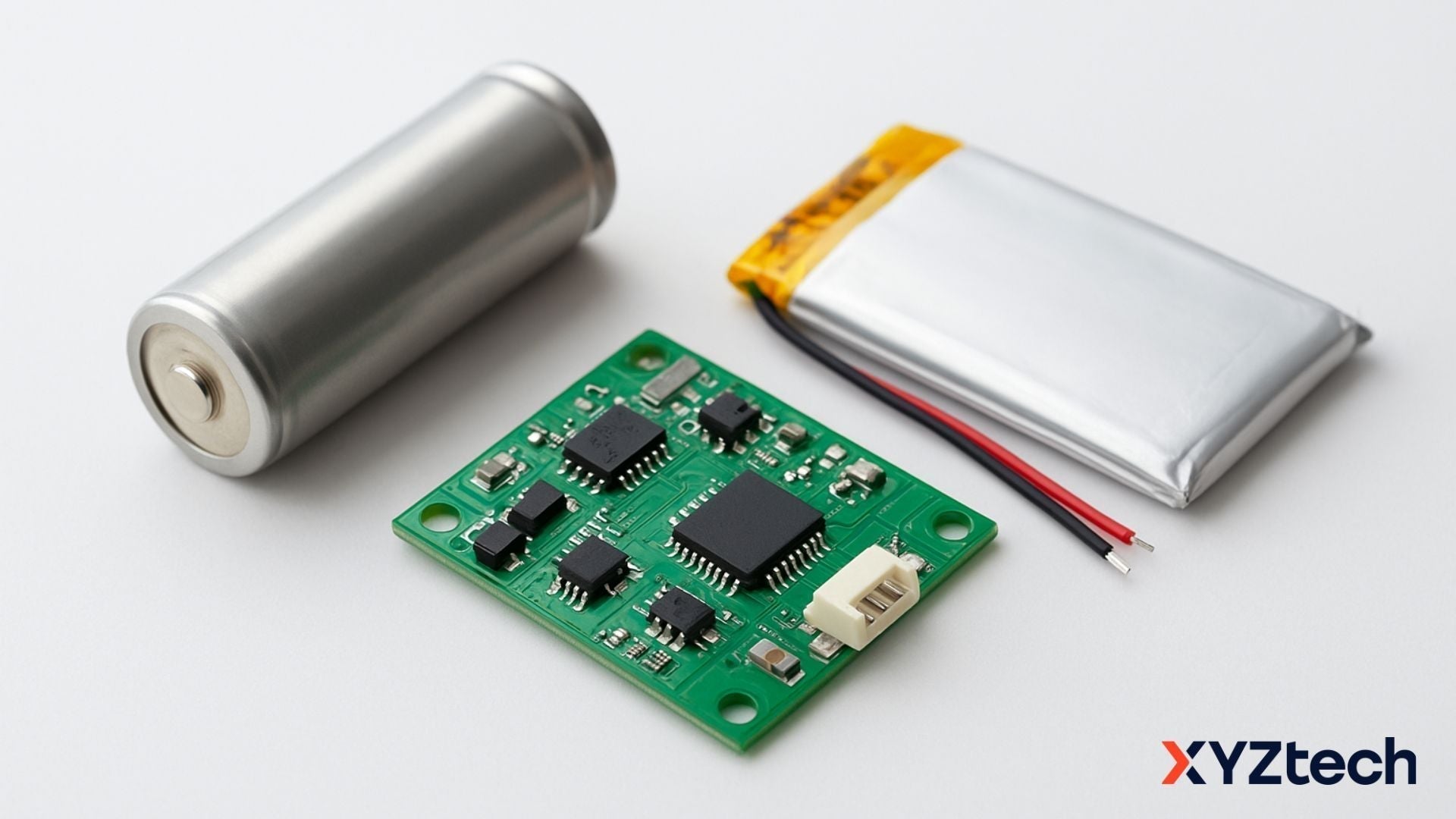
Lithium batteries power everything from smartphones to drones, but their energy density comes with safety risks. That’s why battery circuit protection is essential; it prevents dangerous issues like overcharging, overheating, or short circuits. In this guide, we’ll walk through the four layers of protection: Cell-Level, Circuit-Level, BMS, and External Safeguards, as shown in the hierarchy diagram below.
Whether your device uses cylindrical Li-ion cells or pouch-style LiPo packs, the same safety principles apply.
In this blog:
- Understanding Battery Circuit Protection
- The Role of Lithium Battery Protection Circuits
- Battery Circuit Protection Hierarchy
- Why This Matters for Everyday Devices
- Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s get started!
Understanding Battery Circuit Protection
Battery circuit protection is a system of built-in features that keeps lithium batteries operating safely. These safeguards automatically react to problems like voltage spikes, short circuits, or overheating.
Li-ion cells often include built-in hardware such as:
- PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) thermistors: Increase resistance when overheated.
- CID (Current Interrupt Devices): Permanently cut power if pressure or temperature is too high.
- Vents: Release built-up gas to prevent ruptures.
LiPo cells, with their pouch-style design, rely more on external circuits and strong casings. Both Li-ion and LiPo cells follow strict safety standards like IEC 62133, which ensures safe design, testing, and shipping.
The Role of Lithium Battery Protection Circuits
A lithium battery protection circuit is your battery’s invisible bodyguard. It:
- Prevents damage from deep discharge or overcharging.
- Stops dangerous surges that could harm your device.
- Balances multi-cell packs for better performance and longer lifespan.
Without it, even a simple power surge or charger failure could cause serious damage, or even fire.
Battery Circuit Protection Hierarchy
The diagram below shows four layers of safety:

- Cell-Level: Physical safety is built into each battery cell.
- Circuit-Level: Electronics that manage voltage, current, and temperature.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Advanced control for multi-cell packs.
- External Safeguards: Chargers, cables, and accessories.
Let’s break down each level of protection in detail.
-
Cell-Level Protections
Every lithium cell is built with safety parts inside its structure. These features form the first line of defense:
- Separator design: A thin membrane keeps positive and negative materials apart.
- Shutdown separator: Melts to block current flow if the cell overheats.
- PTC Thermistor: Increases resistance as temperature rises, reducing current flow and preventing further heating.
- CID (Current Interrupt Device): Permanently disconnects power if pressure or heat reaches unsafe levels.
- Vents: Allow gas to escape, reducing the risk of rupture or explosion.
- NTC Thermistors: Monitor temperature changes, triggering a shutdown if needed.
These protections form the first line of defense but are only part of a larger safety system, especially for LiPo packs that lack the hard casing of cylindrical cells.
-
Circuit-Level Safety: The Heart of Lithium Battery Protection
The lithium battery protection circuit, also known as the Protection Circuit Module (PCM), is where most battery safety work happens. This small circuit board uses MOSFETs (electronic switches) controlled by an integrated circuit (IC) to manage voltage, current, and temperature.
Core safety functions include:
- Overcharge/over-discharge cutoffs: Stops charging when full and cuts power if voltage drops too low.
- Short circuit detection: Instantly cuts current during a short to avoid overheating.
- MOSFET switches: These are like electronic gates controlled by the circuit’s IC (integrated circuit). If unsafe conditions are detected, MOSFETs physically block power flow, acting as fast, precise switches.
Many devices use redundant safety features. For example, a MOSFET may work alongside a fuse and thermal sensor. If one system fails, another still protects you, which is why buying quality devices is worth it.
-
Battery Management System (BMS): The “Brain” of Battery Circuit Protection
For multi-cell battery packs, a Battery Management System (BMS) takes safety to the next level. Acting as the battery’s control center, it:
- Balancing: Keeps all cells charged evenly, extending battery life.
- Temperature management: Uses active cooling (fans, heat sinks, liquid cooling) or passive cooling (materials and design) to prevent overheating.
- State-of-charge tracking: Helps your phone or laptop show an accurate battery percentage.
Advanced BMS systems also communicate with devices, sending health reports, charging status, and even warnings if the pack is unsafe. This is why your laptop or phone can alert you when your battery needs service.
Thermal Management: Keeping Lithium Batteries Cool
Heat is a major threat to lithium battery safety and performance. A Thermal Management System (TMS) works hand-in-hand with the BMS and PCM to control temperature:
- Active cooling: Uses fans, liquid cooling, or heat sinks to move heat away from the battery.
- Passive cooling: Relies on battery materials, structure, and casing to release heat naturally.
Devices like electric bikes, drones, and laptops often combine both methods to handle heavy use.
-
External Safeguards: Chargers and Accessories Matter Too
Safety doesn’t end with the battery itself. Manufacturers and users both play a role:
- Certified chargers: Meet standards like IEC 62133, UL, and CE, ensuring devices are safe globally.
- Smart charging chips: Adjust voltage and current for different devices.
- USB standards: USB-C and Power Delivery (PD) regulate fast charging to prevent overheating.
Look for certifications like UN38.3 for transport safety and UL for consumer protection. Reputable brands list these certifications clearly, unlike cheap knockoffs that skip testing.
Why This Matters for Everyday Devices
Every time you plug in your phone, laptop, or power bank, multiple safety layers quietly protect you. Cell-level components stop overheating at the source, circuit boards like the PCM cut off dangerous currents, and the BMS monitors everything in real time. Even your charger plays a role by regulating voltage and following strict safety standards.
Without these systems, a single overcharge, short circuit, or aging battery could lead to failure, or worse, a fire. If your battery is swollen, running hot, or not holding a charge, replace it right away to avoid accidents.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are battery safety certifications important?
Certifications like IEC 62133, UL, and UN38.3 prove that a battery has passed international safety and performance tests. They confirm the product has built-in protections and meets shipping regulations. Choosing certified batteries reduces risks and guarantees better reliability.
How can I tell if a battery is unsafe to use?
Signs of a failing or unsafe battery include swelling, leaking, overheating, or a noticeable drop in capacity. Stop using a damaged battery immediately and dispose of it at an authorized recycling facility. Continuing to use a faulty battery can lead to short circuits or even fire hazards.
How do you know if a battery has a protection circuit?
Protected batteries often appear slightly longer than unprotected ones because the safety board is attached to the base. These batteries also feature an extra connection that links the top and bottom to ensure proper protection. If in doubt, review the battery’s datasheet or product details, as trusted brands highlight this feature.
Final Thoughts on Battery Circuit Protection
Battery circuit protection isn’t just a feature; it’s a multi-layered safety system. From cell-level hardware to advanced BMS communication, these features protect your devices and help batteries last longer.
Understanding these layers, Cell-Level, Circuit-Level, BMS, and External Safeguards, gives you a clear picture of what’s happening behind the scenes, helping you use your gadgets with confidence.
Related Articles
What Is an N52 Magnet? Why It Matters for Wireless Charging
Power Bank Casing Materials: What They Are & Why They Matter
Charger Specifications: Understand Power Bank Specs Like a Pro







